Heavy Rain Expected: Second Half Of The Week
viral.buzzorbitnews
Aug 20, 2025 · 7 min read
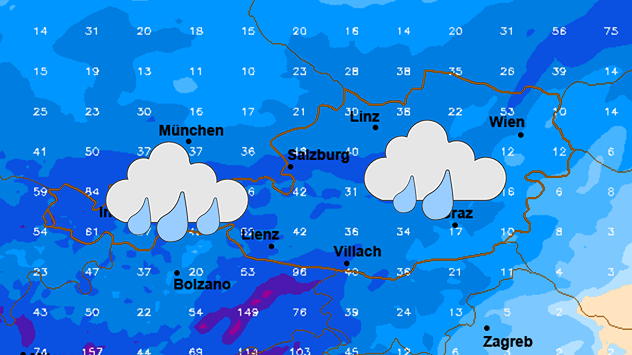
Table of Contents
Heavy Rain Expected: Second Half of the Week
The forecast is in, and it's not looking pretty for many regions. A significant weather system is poised to bring heavy rainfall to several areas during the second half of this week, prompting warnings and advisories from meteorological agencies. This article will delve into the specifics of this incoming storm, outlining its expected impact, providing crucial safety advice, and exploring the scientific reasons behind its intensity. Understanding this weather event is crucial, not just for planning purposes, but also for ensuring your safety and the safety of your community. The potential for flooding, power outages, and travel disruptions is substantial, making preparedness absolutely vital. We'll dissect the anticipated timeline, locations most at risk, and the steps you can take to mitigate potential damage and hazards.
Understanding the Incoming Storm System
The approaching storm system is a complex amalgamation of several atmospheric factors. Let's break down the key elements contributing to the expected heavy rainfall:
-
A Deep Low-Pressure System: At the heart of this weather event lies a deep low-pressure system developing over [Specify the region of origin, e.g., the central Atlantic]. This low-pressure zone creates an area of significantly lower atmospheric pressure than its surroundings, attracting moisture-laden air.
-
High Moisture Content: Warm, humid air masses from [Specify the source region, e.g., the Gulf of Mexico] are being drawn into this low-pressure system. This air is incredibly rich in water vapor, providing the raw fuel for the intense precipitation.
-
Upper-Level Atmospheric Dynamics: The interaction of upper-level atmospheric winds and jet streams plays a critical role. These winds guide the storm's path and intensity, further influencing the amount of precipitation that will fall. The current forecast suggests a [Describe the jet stream pattern, e.g., strong southerly jet stream] will amplify the storm's energy and contribute to prolonged and heavy rainfall.
-
Orographic Lifting: For mountainous regions, the process of orographic lifting will exacerbate rainfall totals. As moist air masses are forced to rise over elevated terrain, they cool and condense, leading to increased precipitation on the windward slopes. This effect can lead to dramatically higher rainfall accumulations in mountainous areas compared to lower-lying regions.
Timeline of the Expected Heavy Rainfall:
The current forecast suggests the heaviest rainfall will begin [Specify the day and time] and continue through [Specify the day and time]. There's a possibility of lingering showers and thunderstorms into [Specify the following day(s)]. However, it's crucial to monitor weather updates closely, as these forecasts can change rapidly based on evolving atmospheric conditions. Specific locations will experience different intensities and durations of rainfall based on their geographical location and the intricate interplay of atmospheric dynamics.
Regional Impacts and Specific Locations at Risk
The widespread nature of this storm system means that several regions will be impacted. Currently, the areas predicted to experience the most significant rainfall include:
-
[Region 1, e.g., Coastal Southern California]: This region is expected to experience [Specify type and intensity of rainfall, e.g., torrential downpours and potential flash flooding]. Low-lying areas and areas with poor drainage are particularly vulnerable.
-
[Region 2, e.g., Central Texas]: [Specify type and intensity of rainfall, e.g., prolonged periods of heavy rain leading to riverine flooding]. River levels are anticipated to rise significantly, posing a threat to communities along major waterways.
-
[Region 3, e.g., Parts of the Appalachian Mountains]: [Specify type and intensity of rainfall, e.g., heavy snow accumulating to significant levels at higher elevations, with potential for landslides]. Orographic lifting will exacerbate precipitation in mountainous areas, increasing the risk of landslides and flooding in valleys.
-
[Region 4, e.g., Parts of the Midwest]: [Specify type and intensity of rainfall, e.g., moderate to heavy rain, potentially leading to localized flooding]. While not as intense as in other areas, the cumulative effect of prolonged rainfall could still lead to significant issues.
These are just a few examples, and it's crucial to check your local weather forecast for the most accurate and up-to-date information specific to your location. The National Weather Service (NWS) and other relevant meteorological agencies will provide detailed alerts and advisories as the storm approaches.
The Science Behind the Storm's Intensity
The intensity of this weather system is a result of a confluence of atmospheric factors that amplify its precipitation potential. The underlying physics involves the processes of:
-
Atmospheric Instability: The presence of a deep low-pressure system creates an unstable atmosphere, where warmer, lighter air is forced to rise above cooler, denser air. This upward movement of air is crucial for cloud formation and precipitation.
-
Condensational Heating: As moisture-laden air rises and cools, the water vapor condenses into liquid water droplets, forming clouds. This condensation process releases latent heat, further warming the air and enhancing its upward motion, leading to a positive feedback loop that intensifies the storm.
-
Convergence and Lift: The converging winds associated with the low-pressure system force air upward, enhancing the lifting mechanism that drives cloud formation and precipitation. This convergence zone acts as a "pump," constantly feeding moisture into the storm system.
-
Moisture Flux: The availability of abundant moisture is paramount. The warm, humid air masses drawn into the storm system provide the essential ingredient for heavy rainfall. The higher the moisture content of the air, the greater the potential for intense precipitation.
These interacting atmospheric processes create a powerful weather system capable of producing significantly heavy rainfall over an extended period.
Safety Precautions and Preparedness
Given the potential for significant impacts, preparedness is key:
-
Monitor Weather Forecasts: Stay updated on the latest forecasts from reliable sources like the National Weather Service (NWS) or your local meteorological agency.
-
Prepare for Flooding: Clear drains and gutters around your home. Move valuable items to higher ground. Know your evacuation routes.
-
Secure Loose Objects: Bring any outdoor furniture or loose objects inside to prevent them from becoming airborne or causing damage.
-
Charge Electronic Devices: Ensure your cell phones, laptops, and other devices are fully charged in case of a power outage.
-
Prepare an Emergency Kit: Have a well-stocked emergency kit including water, non-perishable food, flashlights, batteries, first-aid supplies, and any necessary medications.
-
Avoid Unnecessary Travel: If heavy rain is expected, postpone any unnecessary travel. Driving during heavy rain can be extremely dangerous.
-
Be Aware of Flash Flooding: Flash floods can develop rapidly, even in areas not typically prone to flooding. Never attempt to drive or walk through floodwaters.
-
Stay Informed: Listen to local news and weather broadcasts for updates and warnings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How accurate are these predictions?
A1: Weather forecasts are based on sophisticated computer models that analyze vast amounts of data. However, they are not perfect. The accuracy of a forecast depends on various factors, including the complexity of the weather system and the availability of accurate data. While the forecast provides a strong indication of heavy rain, precise amounts and locations can still vary. It's crucial to continually monitor updates.
Q2: What should I do if I experience a power outage?
A2: If you experience a power outage, avoid downed power lines. Report the outage to your power company. Use flashlights, not candles, to avoid fire hazards. Conserve battery power on electronic devices.
Q3: What constitutes a "flash flood"?
A3: A flash flood is a rapid, sudden flooding of low-lying areas, often caused by intense rainfall over a short period. These floods can develop very quickly, giving little warning. They are particularly dangerous as they can occur unexpectedly and with devastating speed.
Q4: What if I'm trapped in my vehicle during a flash flood?
A4: If you find yourself in a vehicle surrounded by floodwaters, abandon the vehicle if it's safe to do so. Climb to higher ground and seek assistance. Do not attempt to drive through floodwaters – the depth can be deceiving and the current incredibly strong.
Q5: Where can I find the most up-to-date information on this storm?
A5: The most reliable source for weather information is your local National Weather Service (NWS) office or equivalent meteorological agency in your region. You can also refer to reputable news sources that provide detailed weather updates.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The incoming storm system poses a significant threat of heavy rainfall across numerous regions, demanding proactive preparedness and vigilance. Understanding the scientific underpinnings of this event helps to contextualize the forecast and emphasizes the importance of taking necessary precautions. By following the safety guidelines outlined above and staying informed through reliable weather sources, you can minimize potential risks and ensure your safety during this period of inclement weather. Stay tuned for further updates and be sure to check out our other articles on weather preparedness and safety for additional information. Remember, preparedness is your best defense against severe weather.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Brampton Womans Shocking Lottery Win
Aug 20, 2025
-
Afc Teams 1 Reason For 2025 Optimism
Aug 20, 2025
-
Wetterumschwung Gewitter And Regen Was Kommt
Aug 20, 2025
-
Prairie Storm Warning Large Hail Strong Winds Wednesday
Aug 20, 2025
-
Esc Winner Loreen Current Projects And Austria 2026
Aug 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Heavy Rain Expected: Second Half Of The Week . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.