Southeast Alaska Fjord: Major Landslide
viral.buzzorbitnews
Aug 14, 2025 · 8 min read
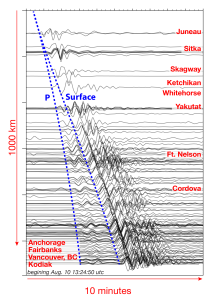
Table of Contents
Southeast Alaska Fjords: Understanding the Threat of Major Landslides
Southeast Alaska's stunning landscape, carved by glaciers over millennia, is characterized by its dramatic fjords. These deep, narrow inlets, ringed by steep, towering mountains, are breathtakingly beautiful but also inherently unstable. The region's susceptibility to major landslides is a significant concern, posing risks to both the environment and the communities that call this area home. This article will delve into the geological processes that contribute to these landslides, explore their impact, discuss ongoing monitoring efforts, and consider future mitigation strategies. Understanding the dynamics of landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords is crucial for ensuring the safety of residents, protecting vital infrastructure, and preserving the ecological integrity of this unique and fragile ecosystem. Failure to address this issue could have devastating consequences, impacting everything from tourism and fishing industries to the delicate balance of the region's natural environment.
Geological Factors Contributing to Landslides in Southeast Alaska Fjords
Several geological factors combine to create a high-risk environment for landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords:
-
Steep Slopes and Topography: The fjords are surrounded by steep, often near-vertical mountain slopes. These slopes, sculpted by glacial erosion, are inherently unstable, especially when weakened by weathering and other geological processes. Even minor seismic activity can trigger catastrophic failures on these precarious slopes.
-
Glacial Processes: The region's history of extensive glaciation is a primary contributor to landslide susceptibility. Glacial carving has left behind a landscape characterized by fractured bedrock, unstable unconsolidated sediments, and steep, over-steepened slopes. The retreat of glaciers has also destabilized previously buttressed slopes, leaving them prone to collapse.
-
Rock Type and Weathering: The bedrock underlying the fjord slopes is often composed of fractured and weakened rocks susceptible to weathering and erosion. Rainfall, freeze-thaw cycles, and the constant pounding of waves contribute to the degradation of these rocks, progressively reducing their strength and increasing their susceptibility to failure. The presence of weak layers within the rock formations further exacerbates the problem, creating zones of weakness that can act as failure planes.
-
Seismic Activity: Southeast Alaska lies within a seismically active region, subject to earthquakes of varying magnitudes. Even relatively small earthquakes can trigger landslides, especially in already unstable areas. The shaking caused by seismic activity can dislodge large masses of rock and sediment, leading to catastrophic slope failures.
-
Water Saturation: Heavy rainfall and snowmelt significantly increase the water content within the soil and rock formations. This saturation reduces the strength of the materials, making them more prone to failure. Groundwater pressure within the slopes can also act as a powerful force, pushing against the slope and contributing to instability. The infiltration of water into cracks and fissures in the bedrock further weakens the rock mass.
Types of Landslides in Southeast Alaska Fjords
Several types of landslides are common in Southeast Alaska's fjords:
-
Rockfalls: These involve the detachment and freefall of individual rock blocks from steep cliffs. While often smaller in scale compared to other types of landslides, rockfalls can still pose significant hazards to infrastructure and navigation in the fjords.
-
Debris Flows: These are rapid flows of unconsolidated sediment, often saturated with water. They can travel at high velocities, carrying large volumes of debris and causing widespread destruction. Debris flows are particularly dangerous due to their speed and unpredictable nature.
-
Rock Slides and Rock Avalanches: These involve the rapid downslope movement of large masses of rock. Rock slides are often characterized by a more coherent movement, while rock avalanches can exhibit more chaotic behavior, involving fragmentation and mixing of rock material. These events can be catastrophic, generating large waves that can inundate coastal areas and damage infrastructure.
-
Subaqueous Landslides: These occur beneath the water surface, often triggered by seismic activity or slope instability. Subaqueous landslides can generate tsunamis, posing a significant threat to coastal communities. They are often difficult to detect and monitor, making them particularly dangerous.
Impact of Major Landslides
The consequences of major landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords can be severe and far-reaching:
-
Loss of Life and Injury: Landslides pose a direct threat to human life, especially in areas with nearby settlements or infrastructure. The rapid movement of debris can crush buildings, bury roads, and trap individuals, resulting in fatalities and injuries.
-
Infrastructure Damage: Landslides can damage critical infrastructure, including roads, bridges, pipelines, and power lines. This damage can disrupt transportation, communication, and essential services, impacting both local communities and regional economies.
-
Economic Impacts: The disruption of transportation, communication, and essential services can significantly impact the region's economy. The tourism industry, a vital component of the Southeast Alaska economy, can be severely affected by landslides, with reduced visitor numbers and damage to tourist facilities. Fishing and other industries can also be negatively impacted by landslide-related disruptions.
-
Environmental Damage: Landslides can cause significant environmental damage, impacting the delicate ecosystem of the fjords. The release of sediment into the water can affect water quality and harm aquatic life. Habitat destruction can also impact various species, including salmon, which are crucial to the region's economy and culture. Landslides can also contribute to coastal erosion and sedimentation.
Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies
Recognizing the significant risk posed by landslides, ongoing efforts are focused on:
-
Geological Mapping and Hazard Assessment: Detailed geological mapping and hazard assessment are crucial for identifying areas at high risk of landslides. This involves assessing slope stability, rock characteristics, and the presence of potential failure planes.
-
Landslide Monitoring Systems: Various monitoring systems, including ground-based instruments (such as inclinometers, extensometers, and GPS receivers), and remote sensing techniques (such as LiDAR and satellite imagery) are used to detect early warning signs of slope instability. These systems provide crucial data for predicting potential landslides and initiating timely evacuations.
-
Early Warning Systems: Effective early warning systems are vital for alerting communities and emergency responders to impending landslides. This involves integrating monitoring data with communication networks to disseminate timely warnings to at-risk populations.
-
Stabilization Techniques: A range of stabilization techniques can be employed to mitigate landslide risk, such as rock bolting, slope grading, and the construction of retaining structures. The specific technique employed will depend on the characteristics of the slope and the nature of the landslide threat. These measures can help to reinforce unstable slopes and reduce the likelihood of future failures.
-
Land-Use Planning: Careful land-use planning is essential for minimizing the risk of landslides. This involves avoiding development in high-risk areas and implementing appropriate building codes and construction practices in areas susceptible to landslides. Regulations can restrict development in vulnerable areas and promote sustainable land management practices.
Scientific Understanding: A Deeper Dive
The scientific understanding of landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords relies heavily on a combination of geological surveys, geotechnical investigations, and advanced modeling techniques. Geotechnical engineers analyze the strength and stability of slopes, utilizing sophisticated computer models to simulate potential failure scenarios. These models incorporate factors such as rock mass properties, groundwater conditions, and seismic activity to predict the likelihood and potential impact of landslides. Isostatic rebound, the gradual uplift of the land after the retreat of glaciers, also plays a significant role in slope instability, as it can reactivate existing faults and create new zones of weakness. Furthermore, researchers are actively studying the influence of climate change on landslide frequency and intensity. Increased rainfall and more intense storms associated with climate change are likely to increase the risk of landslides in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How often do major landslides occur in Southeast Alaska fjords?
A1: The frequency of major landslides varies considerably, influenced by factors like rainfall, seismic activity, and slope stability. While some areas may experience infrequent large-scale events, others might witness more frequent smaller-scale landslides. Comprehensive historical records and ongoing monitoring are essential for accurately assessing landslide frequency and identifying patterns.
Q2: Are there any warning signs that a landslide might occur?
A2: Several warning signs can indicate an impending landslide. These include unusual ground movements, cracking or bulging of the ground, changes in water flow, increased sediment in streams, and unusual sounds, such as cracking or rumbling. It’s crucial to be aware of these signs and report them to the appropriate authorities.
Q3: What should I do if I suspect a landslide is occurring?
A3: If you suspect a landslide is imminent, evacuate the area immediately. Follow established evacuation routes and seek higher ground. If trapped, try to protect yourself from falling debris and contact emergency services as soon as possible.
Q4: Are there any government initiatives to address landslide risk?
A4: Yes, various governmental agencies at the local, state, and federal levels are actively involved in landslide risk mitigation. These efforts include funding research, implementing monitoring programs, and developing early warning systems. Local governments often play a crucial role in land-use planning and community preparedness.
Q5: What role does climate change play in landslide risk?
A5: Climate change is expected to increase the risk of landslides in Southeast Alaska. Increased rainfall, more intense storms, and thawing permafrost can all destabilize slopes and increase the frequency and intensity of landslide events. This necessitates a proactive approach to adaptation and mitigation.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The majestic fjords of Southeast Alaska present a unique and beautiful landscape, but one that requires careful management due to the inherent risks associated with major landslides. Understanding the geological processes driving these events, implementing effective monitoring systems, and employing appropriate mitigation strategies are crucial for protecting both the environment and the communities that thrive in this remarkable region. The ongoing research and collaborative efforts focused on landslide risk reduction are essential for ensuring the long-term safety and sustainability of Southeast Alaska's fjords. To learn more about specific landslide events and ongoing research in the region, we encourage you to explore resources from the USGS, Alaska Department of Transportation & Public Facilities, and other relevant organizations. Staying informed about this ongoing challenge is essential for responsible stewardship of this magnificent environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Kanu Des Manitu Weltpremiere Details And Einblicke
Aug 14, 2025
-
Drowned Swimmer Found In Danube River
Aug 14, 2025
-
Pregame Notes Rain Check
Aug 14, 2025
-
Metro Detroit Severe Thunderstorm Warning What You Need To Know
Aug 14, 2025
-
Canadian Wins Huge Lotto Max Second Prize
Aug 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Southeast Alaska Fjord: Major Landslide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.