Southeast Alaska Fjord: Major Landslide Impact
viral.buzzorbitnews
Aug 13, 2025 · 7 min read
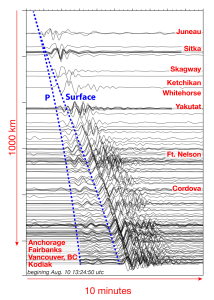
Table of Contents
Southeast Alaska Fjords: Major Landslide Impacts
Southeast Alaska's stunning landscape, carved by glaciers over millennia, is a tapestry of towering mountains, dense rainforests, and intricate fjords. These deep, narrow inlets, once carved by glacial ice, are now vital waterways, supporting rich ecosystems and crucial to the region's economy and cultural heritage. However, this breathtaking beauty belies a significant underlying risk: the ever-present threat of massive landslides. Understanding the impact of these landslides, their frequency, and their cascading effects on the environment, economy, and communities of Southeast Alaska is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and ensuring the long-term sustainability of this fragile yet vibrant region. This article will delve into the significant impacts of major landslides on Southeast Alaska's fjords, examining the geological processes involved, the consequences for the environment and human populations, and the ongoing research efforts aimed at predicting and mitigating future events.
The Geological Setting and Landslide Mechanisms
Southeast Alaska's susceptibility to large-scale landslides stems from a complex interplay of geological factors. The region's rugged topography, steep slopes, intense rainfall, and the legacy of glacial activity all contribute to a high-risk environment. The bedrock itself is often fractured and weakened by past tectonic activity and glacial erosion, making it more vulnerable to slope failure. Furthermore, the region experiences significant seismic activity, with earthquakes capable of triggering or exacerbating landslides.
Several mechanisms can initiate major landslides in Southeast Alaskan fjords:
-
Rainfall-Induced Slope Failure: The region's high rainfall saturates the soil and bedrock, reducing their strength and increasing the likelihood of slope instability. Prolonged periods of heavy rainfall can lead to gradual slope creep, ultimately culminating in catastrophic failure.
-
Seismic Activity: Earthquakes, even relatively small ones, can trigger landslides by shaking loose unstable slopes already weakened by other factors. Larger earthquakes can cause widespread devastation, initiating multiple landslides simultaneously.
-
Glacial Retreat and Isostatic Rebound: The ongoing retreat of glaciers in Southeast Alaska is changing the landscape, leading to increased slope instability. The removal of glacial ice causes isostatic rebound—the land slowly rises as the weight of the ice is removed—which can destabilize slopes and increase the risk of landslides.
-
Undercutting by Water: The action of waves and currents eroding the base of steep slopes along the fjord can lead to undercutting, further destabilizing the slopes and increasing the likelihood of failure. This process is particularly significant in areas where glaciers have recently retreated, leaving behind steep, unstable cliffs exposed to the water.
Impacts of Major Landslides on Southeast Alaskan Fjords
The consequences of major landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords are far-reaching and multifaceted:
-
Tsunami Generation: Large landslides plunging into the water can generate devastating tsunamis. These waves can travel at high speeds, impacting coastal communities and infrastructure along the fjord and potentially even reaching more distant areas. The scale of the tsunami depends on the volume of the landslide and the steepness of the slope into the water.
-
Habitat Destruction: Landslides can completely alter the fjord's underwater landscape, burying benthic habitats and disrupting crucial ecological processes. The resulting sediment plumes can smother marine life, impacting fish populations, shellfish beds, and other organisms vital to the fjord's ecosystem.
-
Water Quality Degradation: The massive influx of sediment from landslides can severely degrade water quality, reducing light penetration and increasing turbidity. This can negatively impact phytoplankton growth, which forms the base of the food web, and potentially lead to harmful algal blooms.
-
Navigation Hazards: Landslides can create significant navigation hazards in the fjords, blocking waterways and potentially damaging vessels. The debris from landslides can also pose a risk to underwater infrastructure such as pipelines and cables.
-
Economic Impacts: The disruption to fishing, tourism, and transportation caused by major landslides can have significant economic consequences for the region. The cost of cleanup and infrastructure repair can also be substantial.
-
Community Impacts: Landslides can pose direct threats to human life and property in coastal communities. The loss of homes, infrastructure, and livelihoods can have profound social and psychological impacts.
Scientific Monitoring and Mitigation Efforts
Scientists are employing various techniques to monitor landslide activity and assess the risk in Southeast Alaska's fjords:
-
Geotechnical Surveys: Detailed studies of slope stability, soil properties, and bedrock geology are crucial for identifying high-risk areas.
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery, aerial photography, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology are used to monitor changes in slope morphology and detect early signs of instability.
-
Seismic Monitoring: Networks of seismic sensors can detect ground vibrations that may precede landslides and provide early warning.
-
Early Warning Systems: Developing reliable early warning systems is crucial for minimizing the impact of landslides. These systems could involve a combination of ground-based sensors, remote sensing, and community-based observation.
Mitigation strategies focus on reducing the risk of landslides and mitigating their impact:
-
Slope Stabilization: Techniques such as terracing, drainage improvements, and rock bolting can help stabilize unstable slopes.
-
Land-Use Planning: Restricting development in high-risk areas is a key element of landslide mitigation. Careful land-use planning can help minimize the exposure of communities and infrastructure to landslide hazards.
-
Community Education and Preparedness: Educating communities about landslide risks and developing emergency response plans are vital for reducing the impact of landslides on human populations.
The Case of the 2015 Taan Fiord Landslide
The 2015 landslide in Taan Fiord serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of these events. This massive landslide generated a significant tsunami, dramatically altering the fjord's landscape and illustrating the complex interactions between geological processes and ecological consequences. This event highlights the need for continued research and improved monitoring systems in Southeast Alaska's fjords. The scientific community continues to study the Taan Fiord event to better understand the triggers, dynamics, and long-term impacts of such large-scale landslides.
FAQ
Q1: How frequent are major landslides in Southeast Alaska's fjords?
A1: The frequency of major landslides varies, influenced by factors such as rainfall, seismic activity, and glacial retreat. While large events are not frequent, historical records and geological evidence indicate that they do occur, making it crucial to understand their potential impacts.
Q2: Can landslides be predicted accurately?
A2: Predicting the precise timing and size of a landslide is currently difficult, though advancements in monitoring techniques are improving our ability to identify areas at high risk and detect early warning signs. Early warning systems are essential in mitigating the impact of these unpredictable events.
Q3: What are the long-term ecological effects of landslides on fjord ecosystems?
A3: The long-term ecological effects can be substantial, impacting biodiversity, altering habitats, and changing nutrient cycles. The recovery of affected ecosystems can be slow and depend on various factors, including the scale of the landslide and the resilience of the affected species.
Q4: What role does climate change play in increasing landslide risk?
A4: Climate change is expected to exacerbate the risk of landslides in Southeast Alaska. Increased rainfall intensity and changes in snowmelt patterns can increase soil saturation and slope instability. Glacial retreat further destabilizes slopes and contributes to undercutting by water.
Q5: What are the ongoing research efforts to address landslide risks?
A5: Ongoing research focuses on improving landslide prediction models, developing more effective early warning systems, enhancing our understanding of the geological processes involved, and exploring innovative mitigation strategies. Interdisciplinary collaborations involving geologists, engineers, ecologists, and social scientists are crucial to address this complex challenge.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The impact of major landslides on Southeast Alaska's fjords is a critical issue demanding continued research, improved monitoring, and effective mitigation strategies. These events pose significant risks to the environment, economy, and human populations. By understanding the geological processes involved, improving prediction capabilities, and implementing robust mitigation measures, we can strive to minimize the devastating impacts of future landslides and ensure the long-term sustainability of this unique and valuable region. To learn more about specific landslide events and ongoing research, visit the websites of the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the Alaska Department of Natural Resources. Stay informed and engaged in protecting this magnificent landscape for future generations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Work Horoscope August 13 2025
Aug 13, 2025
-
Covid 19 Variant Surge Us States Most Affected
Aug 13, 2025
-
Taylor Swift And Travis Kelce New Album And New Heights
Aug 13, 2025
-
Bournemouth Vs Liverpool Match Preview And Prediction
Aug 13, 2025
-
Android Auto 15 Beta Now Available
Aug 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Southeast Alaska Fjord: Major Landslide Impact . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.