## The Science Of Sports Photography:
viral.buzzorbitnews
Aug 10, 2025 · 8 min read
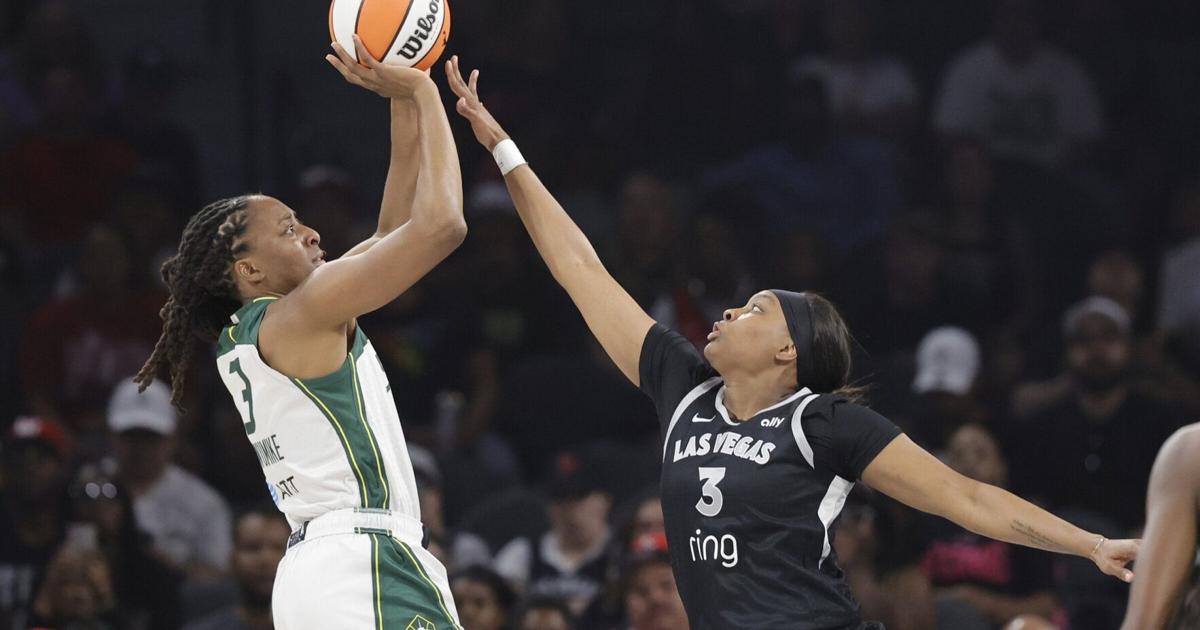
Table of Contents
The Science of Sports Photography: Capturing the Peak of Performance
Sports photography isn't just about pointing a camera and clicking the shutter. It's a complex interplay of technical skill, artistic vision, and a deep understanding of the science behind capturing fleeting moments of intense athleticism. This article delves into the scientific principles underpinning exceptional sports photography, from understanding light and motion to mastering camera settings and post-processing techniques. We'll explore how physics, optics, and even psychology contribute to creating compelling images that truly capture the essence of sporting events. Mastering these principles allows photographers to translate the raw energy and precision of athletes into visually stunning and emotionally resonant photographs. Whether you're a seasoned pro or just starting out, understanding the science behind the art will significantly elevate your sports photography game.
Understanding Light: The Foundation of Every Image
Light is the fundamental element in photography, and sports photography presents unique challenges in harnessing it effectively. The fast-paced nature of sporting events means light conditions can change rapidly, requiring quick adaptation and precise camera settings. Understanding different light sources – natural light (sunlight), artificial light (stadium lights), and their interplay – is crucial.
-
Ambient Light: This refers to the existing light in the environment. In outdoor sports, this is primarily sunlight, which varies drastically throughout the day due to the sun's angle and atmospheric conditions. Understanding the "golden hour" (shortly after sunrise and before sunset) and "blue hour" (twilight) is essential for achieving soft, flattering light. In indoor arenas, artificial lighting is the primary source, often creating uneven illumination and requiring careful consideration of white balance.
-
Light Quality: Hard light, typically produced by direct sunlight, creates harsh shadows and high contrast. Soft light, often found during the golden hour or diffused by clouds, produces gentler shadows and a more even exposure. Understanding light quality allows photographers to choose the best shooting time and position to achieve the desired effect.
-
Light Metering: A crucial aspect of capturing well-exposed images is using the camera's light meter effectively. Different metering modes (evaluative, center-weighted, spot) provide varying levels of control over exposure, allowing photographers to prioritize different parts of the scene. In sports photography, spot metering is often used to precisely measure the light on the subject, ensuring proper exposure even in challenging lighting conditions.
-
Shutter Speed: The duration the camera's shutter remains open, directly impacting motion blur. Fast shutter speeds (1/500s or faster) are critical for freezing action, capturing sharp images of athletes in motion. Slower shutter speeds can be creatively used for motion blur, conveying a sense of speed and dynamism.
Mastering Motion: Freezing Action and Creating Blur
Capturing the dynamism of sports requires a deep understanding of motion and its impact on the final image. The interplay between shutter speed, aperture, and ISO determines how motion is depicted:
-
Freezing Action: As mentioned earlier, fast shutter speeds are paramount for freezing action. This allows photographers to capture sharp images of athletes at the peak of their performance, showcasing precise movements and expressions. This requires high ISO settings, potentially compromising image quality if not managed correctly.
-
Motion Blur: Using slower shutter speeds (while maintaining acceptable sharpness in the subject) can creatively emphasize movement, conveying a sense of speed and dynamism. This technique requires careful planning and precise camera movement to achieve the desired effect, often involving panning to follow the subject.
-
Panning: This technique involves tracking a moving subject with the camera while using a relatively slower shutter speed. This results in a sharp subject against a blurred background, further emphasizing movement and conveying a sense of speed.
-
Aperture and Depth of Field: Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens and influences the depth of field (the area of the image that appears in focus). A wide aperture (low f-number, like f/2.8 or f/4) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background and emphasizing the subject. A narrow aperture (high f-number, like f/8 or f/11) increases the depth of field, keeping more of the scene in focus.
Understanding Camera Settings and Equipment
The mastery of camera settings is essential in sports photography. Understanding the relationship between shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and white balance is crucial for capturing well-exposed, sharp images.
-
ISO: This setting controls the camera's sensitivity to light. Higher ISO settings allow for faster shutter speeds in low-light conditions, but can introduce noise (grain) into the image. Finding the optimal balance between speed and image quality is crucial in sports photography.
-
Aperture Priority Mode (Av or A): This mode allows the photographer to control the aperture while the camera automatically adjusts the shutter speed. It's a useful mode for controlling depth of field, especially when shooting in challenging light conditions.
-
Shutter Priority Mode (Tv or S): This mode allows the photographer to control the shutter speed while the camera automatically adjusts the aperture. This is ideal for freezing action or creating motion blur, giving the photographer precise control over motion depiction.
-
Manual Mode (M): This mode gives the photographer complete control over both shutter speed and aperture. It's the most challenging mode but offers the most creative flexibility.
The Role of Lenses in Sports Photography
Choosing the right lens is crucial for capturing compelling sports images. Different lenses excel in different situations:
-
Telephoto Lenses: These lenses are indispensable for sports photography, allowing photographers to capture detailed images of distant subjects. Longer focal lengths (e.g., 70-200mm, 100-400mm, or even longer) are commonly used to isolate athletes and capture their expressions and movements.
-
Wide-Angle Lenses: While less commonly used for isolating athletes, wide-angle lenses (e.g., 16-35mm) can capture the overall context of the sporting event, showcasing the environment and the atmosphere. They're particularly useful for establishing shots or capturing the energy of the crowd.
-
Prime Lenses: Prime lenses (lenses with a fixed focal length) often offer superior image quality and faster apertures compared to zoom lenses. This can be particularly beneficial in low-light situations.
Post-Processing and Image Enhancement
Post-processing is an integral part of sports photography. Software like Adobe Lightroom and Photoshop allows photographers to enhance their images, correcting exposure, sharpening details, and enhancing colors.
-
Exposure Correction: Adjusting brightness, contrast, and white balance to create a balanced and visually appealing image.
-
Sharpening: Enhancing the sharpness of details, particularly important in fast-action shots where slight blur might be present.
-
Noise Reduction: Minimizing the appearance of grain (noise) that can occur at high ISO settings.
-
Color Grading: Adjusting the overall color palette of the image to create a specific mood or atmosphere.
The Psychology of Sports Photography: Capturing the Emotion
Beyond the technical aspects, successful sports photography requires an understanding of the psychology of the sport and the athletes. Capturing the emotion of the moment is what elevates a good photograph to a great one.
-
Anticipation: Knowing the sport and anticipating key moments allows photographers to be in the right place at the right time.
-
Emotion: Capturing not only the physical action but also the emotions of athletes—joy, frustration, determination—adds depth and meaning to the image.
-
Storytelling: The best sports photographs tell a story, conveying not only the action but also the narrative of the event.
Scientific Principles at Play: A Closer Look
Several scientific principles underpin successful sports photography:
-
Optics: Understanding how light interacts with lenses, affecting image sharpness, depth of field, and overall image quality.
-
Physics of Motion: Understanding motion blur and how to control it using shutter speed and other settings.
-
Color Science: Understanding color temperature and white balance for accurate and visually appealing color representation.
FAQ
Q1: What camera settings are best for freezing action in sports photography?
A1: Generally, a fast shutter speed (1/500s or faster), a high enough ISO to allow for the fast shutter speed (depending on the light conditions), and a suitable aperture (depending on the desired depth of field) are crucial for freezing action.
Q2: What type of lens is best for sports photography?
A2: Telephoto lenses are generally preferred, with focal lengths ranging from 70-200mm to 100-400mm or even longer, depending on the distance to the subject.
Q3: How important is post-processing in sports photography?
A3: Post-processing is essential for enhancing images, correcting minor flaws, and creating a visually appealing final product. It's a crucial step in the overall workflow.
Q4: What are some common mistakes in sports photography?
A4: Common mistakes include using too slow a shutter speed, resulting in blurry images; incorrect white balance, leading to unnatural colors; and not anticipating key moments in the action.
Q5: How can I improve my sports photography skills?
A5: Practice regularly, experiment with different settings, study the work of other successful sports photographers, and learn to anticipate key moments in the action. Consider attending workshops or taking online courses to further enhance your skills.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Mastering sports photography involves a blend of technical proficiency and artistic vision. Understanding the underlying scientific principles – from optics and physics to the psychology of the sport – is crucial for capturing compelling and emotionally resonant images. By mastering light, motion, and camera settings, and by combining technical skill with artistic vision, photographers can truly capture the thrill, excitement, and drama of sporting events. We've only scratched the surface of this multifaceted field; explore more about specific aspects like advanced lighting techniques or post-processing workflows in our upcoming articles. Start experimenting and honing your skills today! What are your biggest challenges in sports photography? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Counterfeit Honey Crushing Austrias Beekeepers
Aug 10, 2025
-
War Of The Worlds A Critical Review
Aug 10, 2025
-
Who Won The Game Insert Winning Team
Aug 10, 2025
-
Peterbot Apologizes Racial Slur Controversy Explained
Aug 10, 2025
-
Close Up Action Shots Of Players
Aug 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about ## The Science Of Sports Photography: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.