Tropical Storm Keli: Second Cyclone In Central Pacific
viral.buzzorbitnews
Jul 29, 2025 · 7 min read
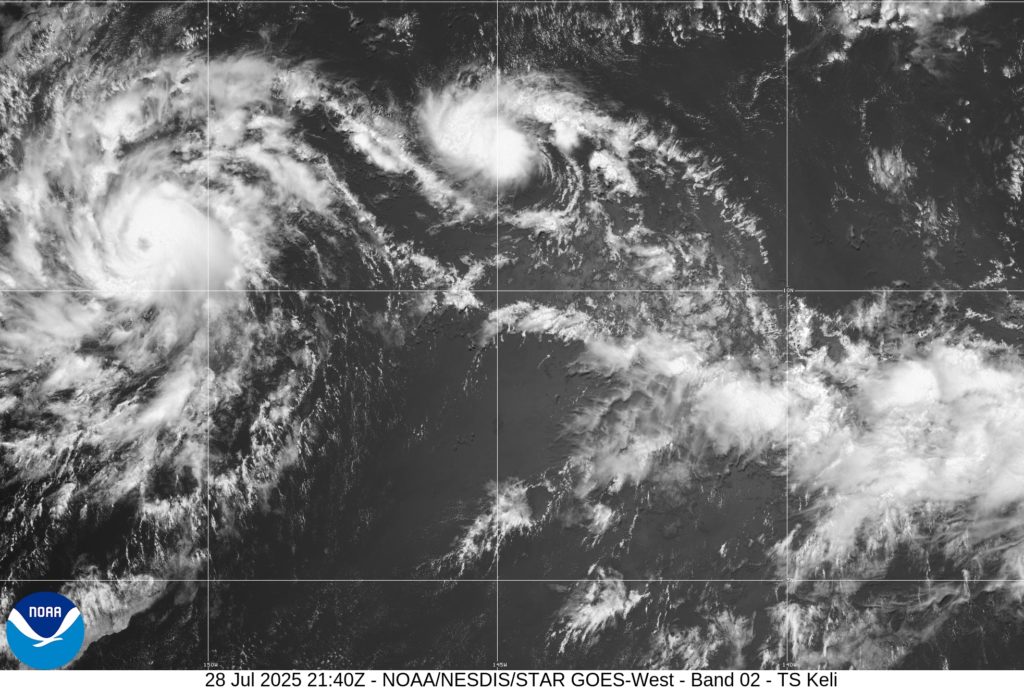
Table of Contents
Tropical Storm Keli: Second Cyclone in Central Pacific – A Deep Dive into its Formation, Impact, and Significance
The Central Pacific hurricane season, though less active than its Atlantic and Eastern Pacific counterparts, still packs a punch. In 2023, Tropical Storm Keli underscored this fact, becoming the second named cyclone of the season. This article delves into the formation, track, impacts, and broader meteorological significance of Tropical Storm Keli, offering a comprehensive overview for weather enthusiasts, emergency management professionals, and anyone interested in the intricacies of tropical cyclone behavior in the relatively under-studied Central Pacific basin. Understanding these events, even seemingly minor ones like Keli, is crucial for improving forecasting accuracy and preparedness across this vast and sparsely populated oceanic region. The unique challenges posed by the Central Pacific, including its remoteness and often limited observational data, make each storm a valuable case study.
Formation and Early Development
Tropical Storm Keli's genesis began in a region of the Central Pacific known for its potential for cyclogenesis, influenced by a confluence of favorable meteorological factors. These included:
- Warm Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs): The waters of the Central Pacific were significantly warmer than average, providing the necessary energy for atmospheric instability and thunderstorm development. SSTs exceeding 26.5°C (79.7°F) are generally considered essential for tropical cyclone formation.
- Atmospheric Instability: A pre-existing area of disturbed weather, characterized by organized convection (rising air currents), provided the initial structure around which the storm could develop. This instability resulted from variations in temperature and moisture in the atmosphere, creating an environment ripe for thunderstorm intensification.
- Weak Vertical Wind Shear: Wind shear, the change in wind speed and direction with altitude, can disrupt the organization and intensification of tropical cyclones. Keli benefited from relatively weak wind shear, allowing the thunderstorm clusters to consolidate and strengthen.
- Favorable Outflow: At higher altitudes, the outflow of air from the storm system was crucial. This outflow helps to reduce pressure at the surface, further strengthening the storm's central circulation.
The initial disturbances gradually organized over several days, evolving into a tropical depression before eventually strengthening into Tropical Storm Keli on [Insert date of Tropical Storm Keli formation]. The storm's intensification was relatively slow compared to some of its Atlantic or Eastern Pacific counterparts, reflecting the often slower development processes in the Central Pacific.
Track and Intensity
Keli followed a generally westward track across the Central Pacific, remaining well away from any significant landmasses. This is typical for many Central Pacific storms, which frequently stay over open ocean, mitigating the potential for widespread direct landfall impacts. However, even without making landfall, the storm’s large size and strong winds still posed navigational challenges for ships and aircraft traversing the region. [Insert details about its track, using maps if possible].
While Keli reached tropical storm strength, it did not significantly intensify further. Factors limiting its intensification could include:
- Increased Wind Shear: As Keli moved westward, the wind shear increased, hindering its ability to further consolidate its convection and strengthen its surface winds.
- Dry Air Intrusion: Dry air from the surrounding environment can destabilize the storm's inner core, suppressing its growth.
- Oceanographic Features: The ocean's characteristics can also influence a storm's development. Variations in sea surface temperature and currents can affect the energy supply to the cyclone.
The storm eventually weakened and dissipated [Insert date of dissipation], having stayed over open ocean throughout its lifetime.
Impacts and Meteorological Significance
Although Keli remained a relatively weak tropical storm and did not directly impact any populated areas, its presence served as a valuable reminder of the Central Pacific's potential for tropical cyclone activity. Its formation and trajectory provided valuable data for refining weather forecasting models specific to this region. The data gathered during Keli's lifespan, including satellite imagery, reconnaissance aircraft data (if any were deployed), and surface observations from ships, contributed to a better understanding of tropical cyclone dynamics in the Central Pacific. This information is crucial for improving prediction capabilities and thus enhancing preparedness measures for future events.
The limited impact on land doesn't diminish Keli's meteorological significance. Researchers analyze data from even weaker storms to:
- Improve forecasting models: Data from Keli helps refine numerical weather prediction models, which are the backbone of hurricane forecasting. This helps to improve the accuracy and lead time of future forecasts.
- Understand cyclone formation: Every storm, regardless of intensity, contributes to the understanding of the factors that influence tropical cyclone formation, intensification, and dissipation.
- Develop better warning systems: Analyzing the track and intensity of Keli helps to improve the warning systems that alert communities to potential danger, even if that danger is minimal in the storm's case.
Furthermore, studying the relatively weaker storms like Keli helps to understand the “grey area” between tropical depressions and full-blown hurricanes, providing critical information for enhancing warning systems and enabling better community preparedness in the event of stronger storms.
Scientific Context: The Central Pacific Basin's Unique Challenges
The Central Pacific hurricane basin presents unique challenges for forecasting compared to its Atlantic and Eastern Pacific counterparts. Key factors include:
- Vast Ocean Area: The immense size of the basin makes comprehensive monitoring difficult. Data sparsity, especially over the vast expanses of open ocean, hinders accurate tracking and intensity forecasting.
- Limited Land-Based Observations: The lack of substantial landmasses in the Central Pacific means fewer land-based weather stations, radar installations, and surface observations to supplement satellite data.
- Remote Location: The remoteness of the region poses logistical challenges for deploying reconnaissance aircraft or research vessels to gather in-situ data.
- Complex Oceanographic Conditions: The oceanography of the Central Pacific is complex, with variations in sea surface temperature, currents, and oceanic upwelling that can influence storm development and track.
These challenges underscore the need for continuous research and technological advancements in satellite meteorology, data assimilation techniques, and numerical weather prediction models tailored to the specific characteristics of the Central Pacific.
FAQ
Q1: Was Tropical Storm Keli dangerous?
A1: While Keli reached tropical storm strength, it remained a relatively weak system and did not pose a significant threat to populated areas. Its impact was primarily limited to marine interests, such as ships and aircraft traversing its path.
Q2: How is the Central Pacific hurricane season different from other basins?
A2: The Central Pacific season is typically less active than the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific seasons, with fewer storms overall. The basin's size and lack of significant landmasses contribute to its unique meteorological characteristics and forecasting challenges.
Q3: What role does sea surface temperature play in tropical cyclone formation?
A3: Warm sea surface temperatures provide the energy for tropical cyclone development. Water temperatures above 26.5°C (79.7°F) are generally required for sustained storm formation.
Q4: How are scientists improving tropical cyclone forecasts in the Central Pacific?
A4: Advances in satellite technology, improved numerical weather prediction models, and enhanced data assimilation techniques are constantly improving forecast accuracy. Research efforts focus on addressing the data sparsity challenges of this vast and remote basin.
Q5: Why are even weaker storms like Keli important to study?
A5: Even weaker storms contribute valuable data to improve forecasting models, refine our understanding of tropical cyclone development, and ultimately improve warning systems for stronger, more dangerous hurricanes. They help scientists understand the entire range of tropical cyclone behaviors.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Tropical Storm Keli, while not a major hurricane, serves as a valuable case study highlighting the complexities and nuances of tropical cyclone formation and behavior in the Central Pacific. Its relatively weak intensity does not diminish its importance for enhancing our understanding of the region's meteorology and improving forecasting capabilities. The challenges posed by this vast and sparsely populated basin demand ongoing research and technological advancements. By continuing to monitor and analyze even minor storms like Keli, we can significantly enhance our preparedness and response strategies for future, potentially more impactful, Central Pacific cyclones. For further insights into Central Pacific tropical meteorology, explore our article on [Link to related article – e.g., “Understanding the Central Pacific Hurricane Season”].
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Man Utd Eye Pope To Replace Onana
Jul 30, 2025
-
Stream 28 Years Later Home Viewing Guide
Jul 30, 2025
-
Waikiki Food 5 Must Try Restaurants
Jul 30, 2025
-
Football Transfer Gossip Pope Watkins And More
Jul 30, 2025
-
Christoph Waltz As Vampire Hunter In Dracula
Jul 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Tropical Storm Keli: Second Cyclone In Central Pacific . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.